Understanding the Survey Process
Have you ever wondered how surveys are conducted and what they entail? Surveys are a fundamental tool for gathering data and insights from a targeted group of individuals. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the survey process, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how surveys are designed, executed, and analyzed.
Survey Design
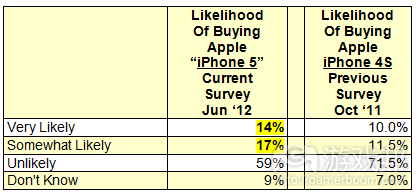
Before a survey can be conducted, it must be carefully designed. This involves determining the survey objectives, identifying the target population, and deciding on the type of survey. There are several types of surveys, including:
-
Quantitative Surveys: These surveys aim to collect numerical data that can be analyzed statistically. They are often used to measure attitudes, opinions, or behaviors.
-
Qualitative Surveys: These surveys focus on gathering in-depth information about opinions, experiences, and motivations. They are often conducted through interviews or focus groups.
-
Online Surveys: These surveys are conducted over the internet and can reach a wide audience. They are cost-effective and can be easily distributed.
-
Mail Surveys: These surveys are sent through the postal service and can reach individuals who may not have internet access.
Survey Instrument Development
Once the survey type is determined, the next step is to develop the survey instrument. This involves creating a set of questions that will be asked to the participants. The questions should be clear, concise, and unbiased. It is important to ensure that the survey instrument is well-structured and easy to understand.
Here are some key considerations when developing a survey instrument:
-
Question Format: Choose the appropriate question format, such as multiple-choice, Likert scale, or open-ended questions.
-
Order of Questions: Arrange the questions in a logical order, starting with easy questions and gradually moving to more complex ones.
-
Response Options: Provide clear and distinct response options for each question.
-
Pretesting: Conduct a pretest of the survey instrument to identify any potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
Survey Distribution
Once the survey instrument is ready, it is time to distribute it to the target population. There are several methods for distributing surveys, including:
-
Online Distribution: Use survey platforms like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms to distribute the survey online.
-
Mail Distribution: Send the survey via postal mail to the target population.
-
Phone Interviews: Conduct phone interviews with participants to gather data.
-
Face-to-Face Interviews: Conduct in-person interviews with participants.
Data Collection and Management
During the survey distribution phase, it is crucial to collect and manage the data effectively. This involves:
-
Monitoring Response Rates: Keep track of the number of responses received to ensure that the survey is reaching the target population.
-
Validating Responses: Ensure that the responses are valid and accurate by checking for inconsistencies or outliers.
-
Storing Data: Store the data securely and organize it for analysis.
Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves:
-
Descriptive Statistics: Calculate basic statistics, such as mean, median, and mode, to summarize the data.
-
Inferential Statistics: Use statistical techniques to draw conclusions about the target population based on the sample data.
-
Qualitative Analysis: Analyze the open-ended responses to gain insights into participants’ opinions and experiences.
Survey Reporting
Finally, it is important to report the findings of the survey. This involves:
-
Summarizing the Key Findings: Provide a clear and concise summary of the survey results.
-
Presenting the Data: Use charts, graphs, and tables to present the data visually.
-
Interpreting the Findings: Discuss the implications of the survey results and provide recommendations for action.
Conclusion
Surveys




